Delivering reliable and scalable applications is super important in today's digital landscape. While building applications, I've encountered numerous situations where efficient task management and execution have been critical to the app. One of the most effective solutions I have found is using a queue architecture. While this can be done with multiple different technologies, I prefer to use Bull MQ and Nest JS. Let's dive into the what, why, and when of queue architecture, and explore how Bull MQ can elevate your application's performance.
What is Queue Architecture?
The queue architecture is a design pattern that manages and processes tasks asynchronously by placing them in a queue. Much like a queue to a restaurant or amusement park ride, each person or task is handled independently. This allows the system to manage workloads efficiently and mitigates the possibility of overwhelming resources. This design pattern is particularly useful in distributed systems where tasks can vary in time and complexity.
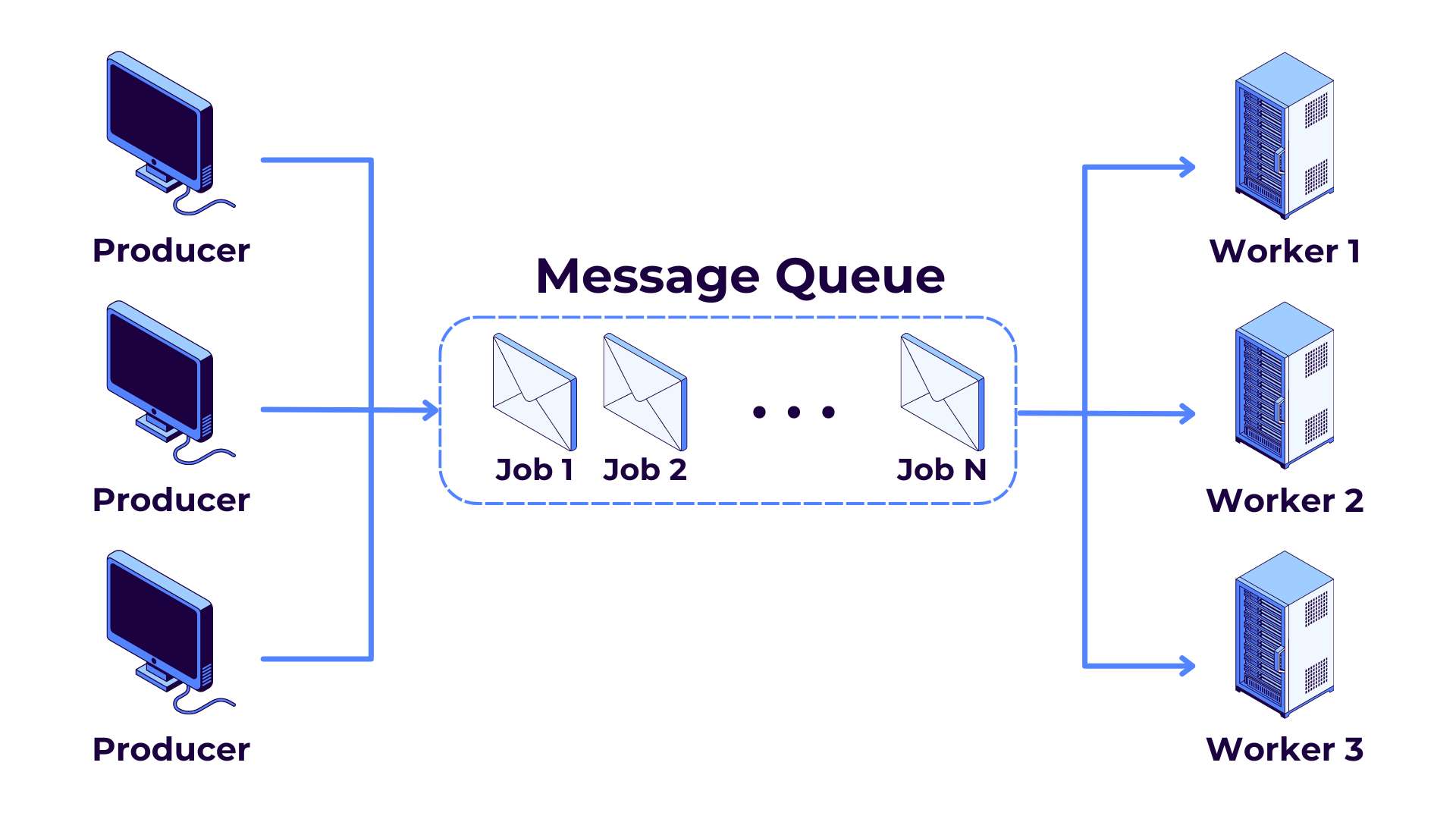
Why Use Queue Architecture?
1. Improved Scalability:
By using a queue architecture, it decouples task generation from task processing. This separation allows you to scale each component independently. This ensures your application can handle an increase in load without degrading performance.
2. Enhanced Reliability:
By queuing tasks, you can ensure they are processed even if there are temporary failures. Queues can act as a buffer that helps mitigate spikes in traffic thus maintaining system stability.
3. Optimized Resource Utilization:
Queues allow for asynchronous task processing. This means that your application can handle multiple tasks concurrently without blocking the main execution threads. This results in a more efficient use of resources and a boost in overall performance.
When to Use Queue Architecture?
Now that we know what the queue architecture is and the benefits, when should we be using it? A good rule-of-thumb that I like to follow is that if the server is processing tasks that are time-consuming or resource intensive, a task queue should be used. Here are a few examples:
- Background Jobs: Sending bulk emails, generating reports, or transcoding a video.
- Rate Limiting: Managing API requests to avoid overloading services.
- Decoupling Services: Ensuring that different microservices communicate asynchronously without direct dependencies.
- Batch Processing: Handing large volumes of data that need to be processed in chunks.
Why Bull MQ with NestJS?
There are a few different queue libraries and services to choose from such as Rabbit MQ, Amazon Simple Queue System (SQS), Apache ActiveMQ, Apache Kafka, and many more. While all of these are good choices, my go to is Bull MQ when working with Nest JS. Bull MQ is a powerful and feature-rich library for managing queues in Node.js applications. When combined with Nest JS, it becomes a robust solution for building scalable and maintainable applications.
Key Features of Bull MQ:
- Priority Support: Allows you to prioritize tasks based on their importance.
- Delayed Jobs: Schedule tasks to be executed at a later time.
- Retries: Automatically retry failed tasks with customizable backoff strategies.
- Concurrency: Process multiple tasks in parallel to maximize throughput.
How to Implement Bull MQ in NestJS?
Integrating Bull MQ with Nest JS is fairly straightforward and involves a few key steps:
- Install Bull:
npm install @nestjs/bull bull - Configure Bull Module: In your
app.module.tsfile, import and configure the Bull module:
import { BullModule } from '@nestjs/bull';
@Module({
imports: [
BullModule.forRoot({
redis: {
host: 'localhost',
port: 6379,
},
}),
BullModule.registerQueue({
name: 'taskQueue',
}),
],
})
export class AppModule {}- Create a Queue Processor: Define a processor to handle tasks from the queue:
import { Processor, Process } from '@nestjs/bull';
import { Job } from 'bull';
@Processor('taskQueue')
export class TaskProcessor {
@Process()
async handleTask(job: Job) { // Task processing logic
console.log(`Processing task ${job.id}`);
}
}- Add Tasks to the Queue: Inject the queue service and add tasks:
import { InjectQueue } from '@nestjs/bull';
import { Queue } from 'bull';
@Injectable()
export class TaskService {
constructor(@InjectQueue('taskQueue') private taskQueue: Queue) {}
async addTask(data: any) {
await this.taskQueue.add(data);
}
}Wrapping Up
Adopting a queue architecture with Bull MQ in Nest JS can enhance the scalability, reliability, and performance of your application. By decoupling task creation and processing, you can build a system that can handle more seamlessly. Whether you're dealing with background jobs, rate limiting , or batch processing, the queue architecture can offer the flexibility needed to manage tasks efficiently.
Implementing Bull MQ in your NestJS application might be the game-changer you need to take your project to the next level. Have you used Bull MQ in your projects? Share your experiences and insights in the comments below!
References:
Feel free to reach out if you have any questions or need further insights on queue architecture and Bull MQ!